PV + Energy Storage: Principles, Advantages, and Application Scenarios
In simple terms, PV (Photovoltaic) + energy storage integrates solar power generation with energy storage systems. As the grid-connected capacity of PV power continues to rise, its impact on the power grid is increasingly prominent, bringing broader growth opportunities for energy storage.
Core Advantages of PV + Energy Storage
Stable and reliable power supply: Energy storage devices function like large batteries, storing excess solar-generated electricity. They supply power when sunlight is insufficient or electricity demand peaks, ensuring an uninterrupted power supply.
Enhanced economic efficiency: Optimized operation increases self-generation and self-consumption of electricity, reducing grid power purchase costs. Energy storage devices can also participate in the auxiliary power service market to generate additional revenue.
Greater flexibility: Energy storage technology makes solar power generation more flexible to meet diverse electricity needs. It can collaborate with virtual power plants to achieve multi-energy complementarity and supply-demand coordination.
Compared with pure grid-connected power generation, PV + energy storage requires additional energy storage batteries and battery charging-discharging devices. Although the initial cost increases to a certain extent, its application scope is much wider. Below are four typical application scenarios based on different use cases:
1. Off-Grid PV Energy Storage Scenario
Application Sites
Remote mountainous areas, off-grid regions, islands, communication base stations, and street lamps.
System Composition
PV array, integrated PV inverter-controller, battery pack, and electrical loads.
Working Principle
When there is sunlight: The PV array converts solar energy into electricity, which powers the loads through the integrated inverter-controller and charges the battery pack simultaneously.
When there is no sunlight: The battery pack supplies power to AC loads via the inverter.
Core Value
Designed for off-grid areas or places with frequent power outages (such as islands and ships), the off-grid system operates independently of the main power grid. Adopting a "store-while-use" or "store-first-then-use" mode, it provides essential power support (like "sending charcoal in snowy weather"). It is highly practical for households in off-grid or power-outage-prone areas.
2. Grid-Connected/Off-Grid PV Energy Storage Scenario
Application Sites
Areas with frequent power outages, regions where surplus self-generated PV electricity cannot be fed into the grid, locations with high self-consumption electricity prices, or areas with significant peak-valley price differences.
System Composition
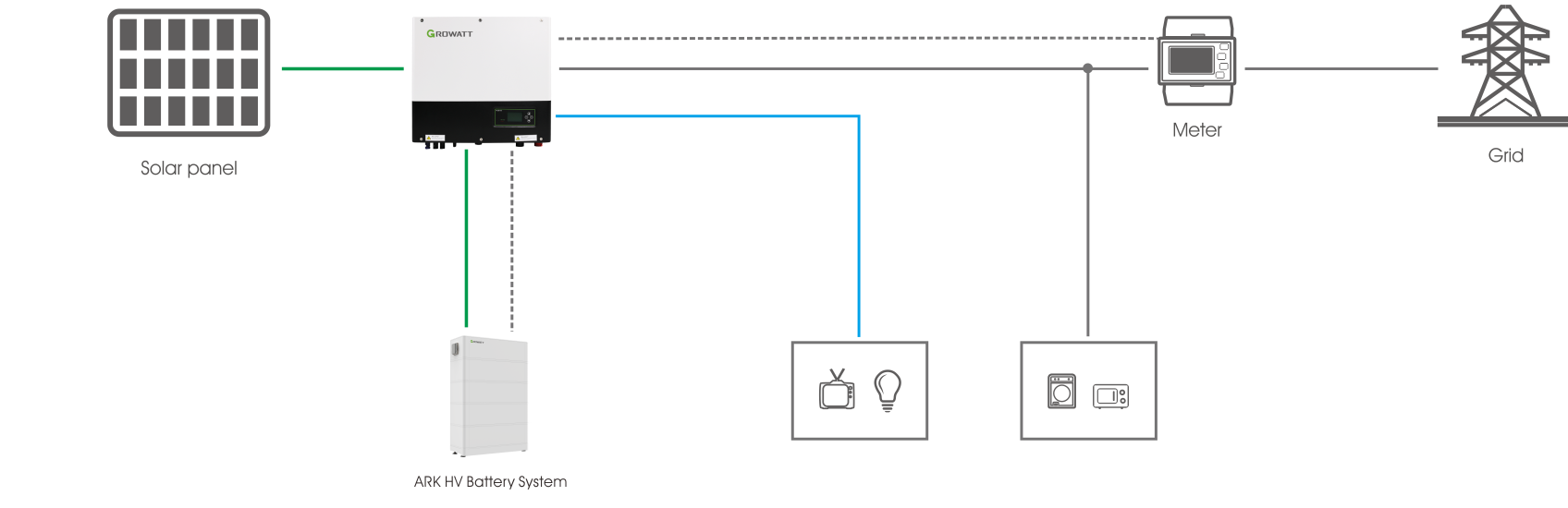
PV array (composed of solar modules), integrated grid-connected/off-grid solar inverter, battery pack, and loads.
Working Principle
When there is sunlight: The PV array converts solar energy into electricity, which powers the loads through the integrated inverter-controller and charges the battery pack.
When there is no sunlight: The battery pack supplies power to the integrated inverter-controller, which then powers AC loads.
Core Value
Compared with grid-connected systems, this system adds a charging-discharging controller and battery pack, increasing the cost by approximately 30%-50%, but with a wider application scope:
Output at rated power during peak electricity prices to reduce electricity expenses.
Charge during off-peak hours and discharge during peak hours to profit from peak-valley price differences.
Switch to off-grid mode as a backup power source during grid outages, with PV and batteries powering loads via the inverter.
This scenario is currently widely applied in developed countries overseas.
3. Grid-Connected PV Energy Storage Scenario
Application Sites
Ground-mounted PV with energy storage, industrial and commercial PV energy storage projects.
System Composition
PV array (composed of solar modules), grid-connected inverter, battery pack, PCS (Power Conditioning System), and electrical loads. It typically operates in an AC-coupled PV + energy storage mode.
Working Principle
When solar power is less than load power: The system is powered by both solar energy and the grid.
When solar power exceeds load power: Part of the solar energy powers the loads, and the rest is stored through the PCS.
Core Advantages
Improved PV utilization rate: Smoothes PV output fluctuations caused by weather and geographical conditions, and supplies energy to the grid under low-light conditions.
Enhanced grid stability: Realizes real-time monitoring and regulation of the grid, with energy storage devices responding quickly to absorb or supply surplus power during grid fluctuations.
Promoted new energy absorption: Improves the grid's capacity to connect and absorb new energy (such as PV and wind power), alleviating peak-shaving pressure through smooth power output.
Diversified profit models: Enables peak-valley arbitrage and demand management to increase system profitability.
As an emerging clean energy application scenario, it has attracted significant attention in China's new energy market for its efficient use of clean energy.
4. Microgrid Energy Storage System Scenario
Core Role
As an important energy storage device, it plays an increasingly critical role in China's new energy development and power system. Its application scenarios continue to expand with technological progress and the popularization of renewable energy.
Key Application Directions
Distributed generation and energy storage systems: Small-scale power generation equipment (such as PV and wind power) is built near users. Surplus electricity is stored in energy storage systems to supply power during peak demand or grid failures.
Microgrid backup power: Provides stable power supply as a backup in remote areas, islands, mines, metallurgy, petrochemical facilities, and temporary construction sites where grid connection is difficult.
Core Value
Through multi-energy complementarity, microgrids give full play to the potential of distributed clean energy. They mitigate drawbacks such as small capacity, unstable power output, and low reliability of independent power supply, ensuring safe grid operation as a valuable supplement to the main power grid. Microgrids are highly flexible, with scales ranging from several kilowatts to dozens of megawatts, and have a wide application scope.
PV + energy storage has diverse application scenarios covering off-grid, grid-connected, and microgrid modes. Each scenario has unique advantages, providing users with stable and efficient clean energy. With the continuous development of PV technology and cost reduction, PV + energy storage will play an increasingly important role in the future energy system. The promotion of these scenarios will also drive the rapid development of China's new energy industry, contributing to energy transition and green low-carbon development

